Not only are they key to surviving, but they're key to THRIVING. Our bodies are mystical, wonderful, and complex. One of the beautiful recent discoveries is that osmolytes are a key driver in maintaining health during periods of dehydration. I think that understanding osmolytes better can lead to amazing insights into strategies and supplementation when it comes to dry fasting. I hope you agree too!
What are osmolytes?
Osmolytes are a group of small, highly soluble molecules that play an essential role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, particularly under stress conditions such as dehydration or extreme temperature fluctuations. These compounds are pivotal in the cell's adaptive response, helping to stabilize proteins, preserve cellular structures, and ensure the proper functioning of various biological processes. Their ability to modulate the cell's hydration state without interfering with normal biochemical reactions makes them crucial for cell survival and adaptation.

Why are osmolytes important to dehydration and dry fasting?
In the context of dehydration, osmolytes assume a vital role. Cells can lose water under various stress conditions, leading to potentially harmful increases in the concentration of proteins and other macromolecules. Osmolytes counteract these effects by balancing the intracellular pressure, thereby protecting cellular structures and maintaining the functionality of proteins. They achieve this by either directly stabilizing proteins or by adjusting the hydration layer around them, thus preserving the delicate balance within the cellular environment.
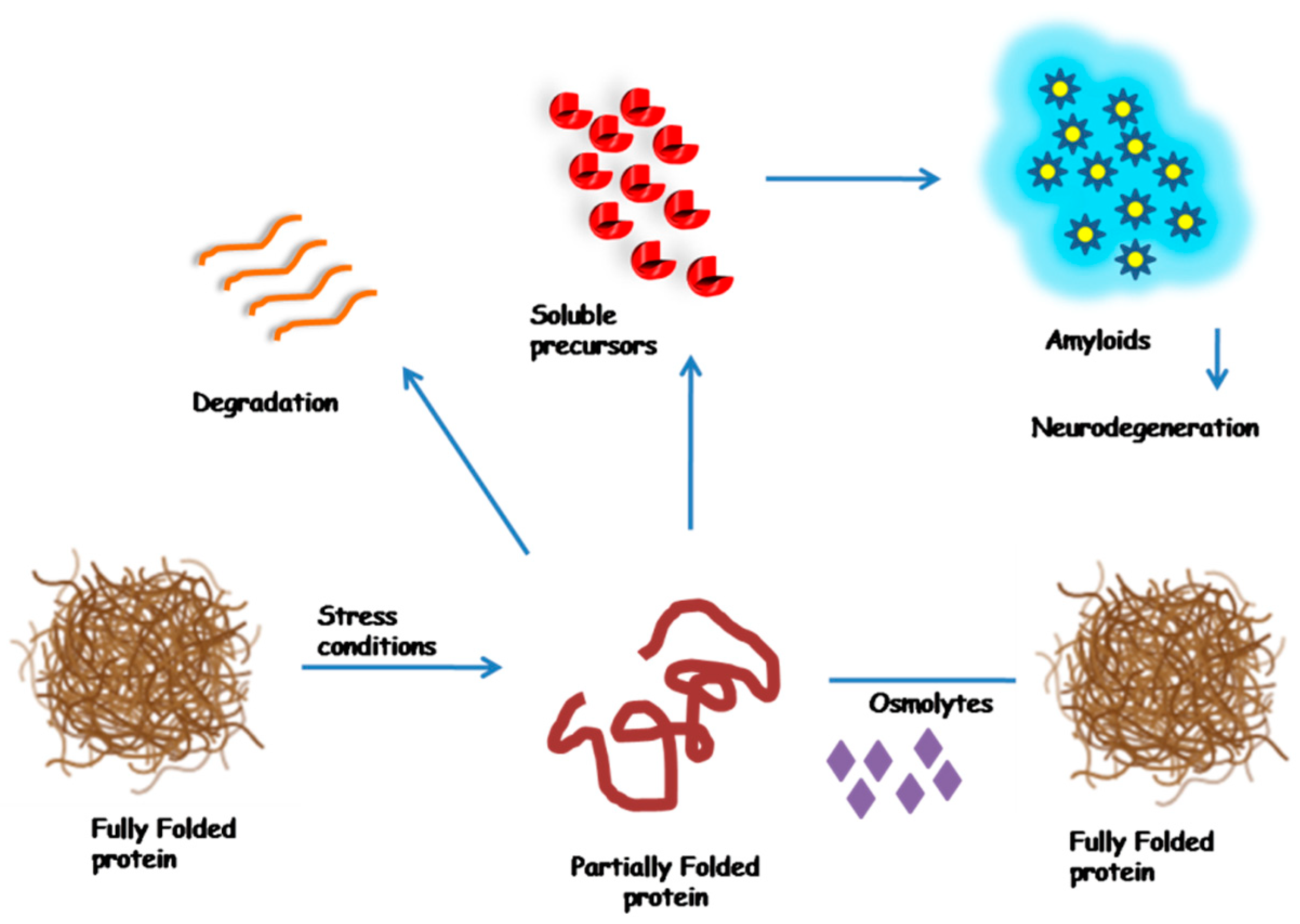
The relevance of osmolytes extends to the concept of dry fasting, a practice where both food and water intake are restricted. During dry fasting, the body must control its water and internal pressure. Osmolytes are key to this. Osmolytes contribute to this process by helping cells retain water and maintain function under conditions of limited external water supply. This protective mechanism is the reason why we can survive long periods of dehydration, where the preservation of cellular integrity and function is critical.
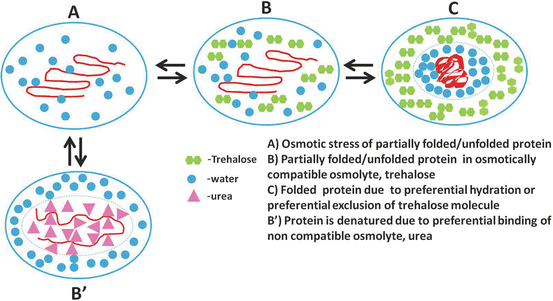
Where to start if you want to consider supplementing osmolytes?
In the human body and diet, several osmolytes are commonly encountered, each playing a unique role in cellular protection and homeostasis.
- How can one ensure a balance of these osmolytes in the body before starting a dry fast?
- How does prolonged dry fasting affect the levels and function of osmolytes in the body?
- Are there specific osmolytes that are particularly beneficial during dry fasting?
- Are there signs or symptoms that might indicate an imbalance or deficiency of osmolytes during a dry fast?
- Are there recommended supplements or foods rich in osmolytes that one should consider before or after a dry fast?
- What are the risks or potential side effects of supplementing with osmolytes?
- Can the presence of certain osmolytes make dry fasting safer or more effective?

Urea is actually an osmolyte too which is neat, and completely the opposite of mannitol - has no negative side effects on kidney cells. But we can't supplement it, so it's not on the list. We also wouldn't want to supplement it because it's chaotropic, lol. Don't drink it! Unless you're trapped in a coal mine. 😄
Osmolytes protect from dehydration and prevent age-related cellular diseases.
There's research that examines how the structure of water inside cells plays a role in aging, how cells process energy, and how they repair themselves, especially in relation to aging and certain diseases. A key theory is that as we age, or when certain diseases are present, the water inside our cells loses its organized structure. This loss may slow down the cell's energy processes and hinder its ability to repair itself, which could contribute to aging and disease progression.

Central to this topic is anhydrobiosis, which is the ability of some organisms to survive extreme dehydration. This survival is linked to substances called osmolytes. Studying these osmolytes and the organisms that use them might help us develop new ways to slow down aging and fix the cell problems that come with it.
Structured Water and EZ Water

Studies suggest that not just adding osmolytes, but also creating a state of hyperosmolarity (similar to dehydration) inside cells, could be beneficial. This state is thought to remove disorganized water from cells and encourage the absorption of osmolytes. This change could help restore normal cell functions, especially in cancer cells. The idea is to shift from disorganized to organized water inside the cell. This shift might bring back a balanced and orderly state in the cell's energy system. However, when cells are pushed too far, they might reach a near-death state, showing how critical balance is for cells.

The research suggests that certain treatments could help fix the damage in cells caused by water that's not properly organized. These treatments work by:
- Inducing peritumoral hyperosmolality: Making the area around a tumor have a higher concentration of certain particles to help pull structured water into the cells. Dry fasting helps here by drying out the tumor cells, weakening them, and allowing for cancer treatment drugs to be better uptaken into these cells. Osmolytes protect the good cells, while the bad ones die out.
- Increasing intracellular kosmotropic osmolytes: Adding substances inside the cells that help organize water and improve cell function. Osmolytes will increase structured water.
- Promoting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation: Boosting a process in the cell's powerhouses (mitochondria) that helps produce energy efficiently. So, osmolytes will help in improving ATP levels and mitochondrial health.

Higher acidity in the body during fasting conditions can increase the abundance of H+ (hydrogen ions) in the body. This is often due to the accumulation of acidic metabolic byproducts such as ketone bodies. This plays an important role in mitochondrial health. So acidic states are therapeutic, but we don't want to be in acidic states forever because of topics like mineral issues, cortisol, and electrical charge. Cells need electron-donor water. Think Hydrogen water, but manage a low-carb diet with alkaline low-carb foods.
These actions aim to organize the water inside the cells properly, which helps the cells work better and restore their energy levels. The idea is that making the water inside cells more structured, can help start a process called apoptosis, where cells are programmed to die when they're not needed anymore. This process is important because it's often not working correctly in cancer cells, allowing them to grow uncontrollably. So, fixing the water structure inside cells might help treat diseases like cancer by making the cells behave normally again.
This research shows that it's really important to keep water inside cells well-organized. This helps cells keep their energy up and repair themselves properly, which is especially useful as we get older or deal with certain illnesses. By studying how some organisms manage to survive in very dry conditions and how increasing particle concentration in cells can rearrange water inside them, we can discover new ways that might slow down aging and make sick cells healthier. This area of study is called anhydrobiosis.
What is anhydrobiosis and how does it correlate to immortality?
Anhydrobiosis is like a survival trick some tiny organisms use to live without water. They dry up completely, and stop all body activities, but can come back to life when they get water again. These organisms can handle losing almost all their water. There's a certain point where if they lose too much water (less than 10% of their body), it's usually too much for most organisms, and they can't survive. But, anhydrobiotic organisms, like some bacteria, can go even lower, to about 2% water, and still manage to revive later.